When you hear the word cyst in your liver, your mind may immediately jump to cancer. That’s natural. The liver is a vital organ, and anything unusual there can feel frightening.
But here’s the good news: most hepatic cysts are NOT liver cancer.
Still, confusion is common. So let’s clear the air. In this detailed guide, we’ll talk about what a hepatic cyst really is, whether it can turn into cancer, and when you should worry. If you or someone in your family has been diagnosed with a liver cyst, this article is for you.
Think of it like this:
Your liver is like a busy factory. A cyst is often just a small water balloon sitting quietly in a corner. Cancer, on the other hand, is like a faulty machine that keeps multiplying and damaging everything around it. Very different things.
Worried about a hepatic cyst? Learn whether it’s cancerous, understand the symptoms, and discover treatment options. Get trusted guidance from Dr Neerav Goyal, recognized as one of the best liver transplant surgeons in India for advanced liver care.
Let’s break it down step by step.
.1 What is Hepatic Cyst?
A Hepatic cyst is a cyst filled with fluid within the liver. It typically contains clear liquid and is generally harmless.
Most people don’t realize they have it since it doesn’t cause any symptoms. It’s typically discovered by accident when you have either an ultrasound scan or CT scan that is done for another reason.
The most frequent liver cysts can be classified as:
Small
Non-cancerous
Slow-growing
Not painful
2. Are Hepatic Cysts the Most Common?
They are popular.
Studies have shown that between 5 and 10 percent of people could suffer from liver cysts, particularly when they get older. The majority of cases are observed among people over 40.
Women are likely to get them more frequently than men.
What is the most important thing to keep in mind?
Most liver cysts do not cause any problems.
3. What is Hepatic Cyst the cause of Liver Cancer?
Let’s tackle the primary query clearly:
It’s not a problem, a normal Hepatic cyst isn’t liver cancer.
Simple cysts:
Is stuffed with fluid
It has walls with thin walls
Does not cause any spread
Does not infiltrate other tissues.
Liver cancer, like Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), behaves quite differently. It is a very aggressive cancer that damages the liver tissue.
However there are many cysts that are not simple. Sometimes, complex cysts might require further examination to determine if they are cancerous.
This is why a thorough assessment is so important.
4. Different types of Liver Cysts
Simple Liver Cysts
The most common
Harmless
Most often, you do not require any treatment.
Polycystic Liver Disease
Genetic disorder
Multiple cysts in the liver
May cause enlargement
Hydatid Cysts
It is caused by parasite infections
More important
The need for treatment
Cystic Tumors
Rare
Could look like cysts, however, they could also be cancerous
Knowing the kind of cyst is essential to deciding which next action to follow.
5. What is the cause of Hepatic Cysts?
The majority of small cysts tend to be congenital which means that you are born with them. They develop slowly over time.
Other causes are:
Parasitic infections
Genetic disorders
Liver injury
Blocked bile ducts
In a lot of cases the reason for this is not known.
6. The symptoms of liver Cysts
A majority of people do not feel anything.
If a cyst gets to be large (more than 5 centimeters) it could be a sign:
Upper right abdominal pain
Bloating
Fullness
Nausea
Liver enlargement
Rarely, severe symptoms occur. However, they could include:
Sudden sharp pain (if cyst ruptures)
Fever (if you are infected)
If symptoms are evident be aware of them.
7. How do doctors diagnose Hepatic Cysts?
Diagnostic tests usually involve imaging:
Ultrasound
The first and most commonly used test. The test is fast and painless.
CT Scan
Provides high-quality pictures.
MRI
If doctors suspect that something is not quite right.
Doctors examine:
Size
Shape
Wall thickness
Solid components
If the cyst appears suspicious, additional tests could be required.
8. What are the signs to be concerned about?
It is recommended to seek out a liver specialist:
The cyst is big.
There is a persistent pain
The cyst develops rapidly.
There are areas of solidity within the cyst.
You already have liver disease
People suffering from cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis require more frequent monitoring due to the fact that their risk of liver cancer is greater.
9. Does a Hepatic Cyst develop into cancer?
This is the truth:
Simple cysts don’t change to cancer.
However, rare cystic tumors, such as cystadenocarcinoma or biliary cystadenoma could appear like normal cysts when scanned.
Expert evaluation is crucial.
If you’re uncertain regarding your diagnosis, obtaining an additional review from the top liver transplant surgeons in India or a reputable liver specialist could give you assurance.
10. Alternative Treatments for Hepatic Cysts
Treatment depends on symptoms.
No treatment is required
Most cysts are not complicated and need no treatment.
Medication
Only used in cysts that are parasitic.
Aspiration
Fluid is removed using needle (temporary solution).
Surgery Removal
It is required If:
Cyst is a very big
Causes pain
It is then infected.
Suspicious for cancer
Laparoscopic surgery that is minimally invasive is widely used in the present.
11. When is Liver Surgery Required?
Surgery isn’t common but could be necessary if:
The cyst compresses nearby organs.
There is bleeding within the cyst.
It is impossible to rule out cancer.
There are many large cysts
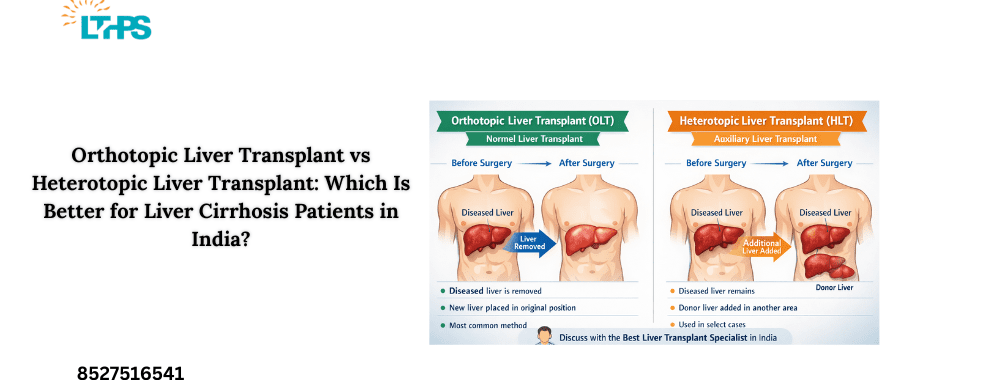
In the most extreme instances of severe damaged liver, a liver transplant could be thought of.
The choice of the most effective liver transplant specialist in India will guarantee:
Accurate diagnosis
Advanced surgical treatment
Better outcomes for recovery
India is now a world-class liver surgery center that has the highest level of expertise.
12. The role of a liver specialist
The liver specialists (hepatologist) assists in:
Accurate diagnosis
Monitoring growth of cysts
Differentiating benign vs cancerous lesions
Recommend treatment
Do not be anxious when you read your scan report. Let a professional read it correctly.
13. Lifestyle and Prevention Tips
While it isn’t always possible to prevent liver cysts, it is possible to keep your liver in good shape.
Healthy Diet
Eat fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grain cereals.
Limit Alcohol
The excess alcohol damage the liver cells.
Maintain Healthy Weight
Obesity can lead to the fatty liver disease.
Regular Check-ups
Particularly if you suffer from cirrhosis or hepatitis.
Your liver is silent all day. It is similar to taking care of your car before it fails.
14. Final Thoughts
Then, is it hepatic cyst liver cancer?
In most cases, absolutely not.
A common hepatic cyst is typically harmless and will not develop into cancer. However, a proper diagnosis is essential to rule out complicated cysts.
If you are experiencing symptoms or are at risk for developing like chronic liver disease consult a liver specialist. If you require more advanced treatment required, consulting the most experienced liver transplant surgeon in India could be the key to success.
Be aware that knowledge decreases anxiety. The more you know about your circumstances and the better you feel.
Commonly asked questions (FAQs)
1. Does a benign hepatic tumor be transformed into cancer?
Hepatic cysts that are simple are not cancerous. However, more complex cysts might require evaluation.
2. Do all liver cysts need surgery?
The majority of liver cysts are not a need for surgical intervention unless they cause symptoms or develop complications.
3. What can I do to determine if my cyst in my liver is a risk?
Imaging tests such as the ultrasound test, CT and MRI aid in determining whether the cyst is simple or complex.
4. How big is a cyst in the liver which is in need of treatment?
Cysts greater than 5 cm with symptoms might require treatment.
5. Do I need to consult with the top liver transplant doctor in india to treat an liver cyst?
Most cysts that are simple don’t require transplant surgery. However should the cyst be massive, complex or is associated with serious liver disease, consulting an expert is suggested.