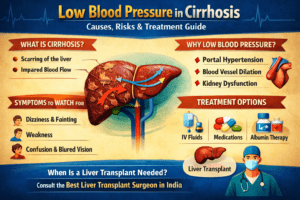
Living with liver cirrhosis can feel like walking on thin ice. Just when you think you understand one problem, another pops up. One of the most confusing — and sometimes dangerous — issues is low blood pressure in cirrhosis.
You might wonder, “Isn’t high blood pressure the real problem?” In many cases, yes. But when it comes to advanced liver disease, low blood pressure (hypotension) can become a serious concern.
In this guide, we’ll break everything down in simple words. We’ll talk about why it happens, what symptoms to watch for, and how it’s treated. If things become severe, we’ll also touch on when liver transplant becomes necessary — and why choosing the best liver transplant surgeon in India can make all the difference.
Let’s get started.
Understanding Cirrhosis and Blood Pressure
Cirrhosis is the final stage of long-term liver damage. Healthy liver tissue gets replaced by scar tissue. This scarring blocks normal blood flow through the liver.
Now here’s the interesting part: when blood can’t pass easily through the liver, your body reacts in unusual ways. Blood vessels in other areas widen. Fluid shifts. Hormones change. All this can lead to low blood pressure.
In simple words, the body tries to “compensate,” but sometimes it overdoes it.
What Is Low Blood Pressure?
Low blood pressure (hypotension) generally means a reading below 90/60 mmHg.
But numbers alone don’t tell the full story.
You may have low BP if you experience:
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Confusion
In cirrhosis patients, low BP can be more dangerous than in healthy individuals because it may signal serious internal complications.
Why Does Cirrhosis Cause Low Blood Pressure?
Let’s break it down.
- 1. Widened Blood Vessels
- Cirrhosis causes the body to release chemicals that widen blood vessels. When vessels expand too much, pressure drops.
- Imagine water flowing through a narrow pipe versus a wide pipe. The pressure falls in the wider one. That’s what happens inside your body.
- 2. Fluid Loss
- Many cirrhosis patients take diuretics (water pills) to control swelling and ascites. Too much fluid loss can lower BP.
- 3. Internal Bleeding
- Cirrhosis can cause enlarged veins (varices) in the food pipe or stomach. If they bleed, blood pressure can drop suddenly.
Role of Portal Hypertension
One major complication of cirrhosis is portal hypertension– increased pressure in the portal vein.
Because blood can’t flow properly through the scarred liver, pressure builds up. To cope, the body diverts blood elsewhere, leading to systemic blood vessel dilation.
This redistribution reduces effective blood volume, causing hypotension.
It’s like traffic being redirected from a blocked highway onto smaller streets. Chaos follows.
Impact on Kidneys (Hepatorenal Syndrome).
One serious complication is Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS).
When blood pressure drops significantly, the kidneys receive less blood. Over time, kidney function declines.
Symptoms include:.
- Reduced urine output.
- Swelling.
- Confusion.
- Severe weakness.
- HRS is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms You Should Never Ignore.
Low blood pressure in cirrhosis isn’t always mild. Watch for:.
- Frequent fainting.
- Sudden confusion.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Cold, clammy skin.
- Severe weakness.
If these appear, seek emergency care immediately.
Risks of Untreated Low BP in Cirrhosis.
- Ignoring low BP can lead to:.
- Kidney Failure.
- Reduced blood supply damages kidneys permanently.
- Shock.
- Severely low pressure can cause circulatory shock.
- Brain Dysfunction.
- Poor blood flow affects mental clarity.
- Increased Mortality.
Advanced cirrhosis with hypotension significantly increases risk of death.
This is why early management is crucial.
- Diagnosis and Monitoring.
- Doctors evaluate:.
- Blood pressure readings.
- Blood tests.
- Kidney function tests.
- Ultrasound scans.
- Endoscopy (to check for varices).
- Regular monitoring helps prevent emergencies.
- Home BP monitoring can also help patients stay alert to changes.
- Medical Treatment Options.
- Treatment depends on the cause.
1. Adjusting Medications.
Diuretics may be reduced if they are causing excessive fluid loss.
2. IV Fluids.
If dehydration is present, fluids are given carefully.
3. Albumin Infusion.
Albumin helps pull fluid back into blood vessels, improving circulation.
4. Vasoconstrictor Drugs.
These medicines narrow blood vessels and raise BP.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes.
You can play a role in managing your condition.
- Stay Hydrated (But Carefully).
- Don’t self-restrict fluids unless advised.
- Avoid Alcohol Completely.
- Alcohol worsens liver damage.
- Follow Low-Salt Diet.
- Prevents fluid buildup without worsening BP.
- Stand Up Slowly.
- Prevent dizziness and falls.
- Small changes can make a big difference.
When Is Hospitalization Needed?
Immediate admission is required if:.
There’s internal bleeding.
Severe kidney dysfunction occurs.
Persistent fainting happens.
BP remains critically low.
Timely hospital care can be life-saving.
Liver Transplant as a Permanent Solution
For advanced cirrhosis, medicines may only offer temporary relief.
In such cases, liver transplantation becomes the definitive treatment.
A successful transplant restores normal blood flow, corrects hormonal imbalances, and improves blood pressure regulation.
If you or your loved one has advanced liver failure with complications like hypotension and kidney dysfunction, consulting the best liver transplant surgeon in india can offer hope and long-term survival.
India has world-class transplant centers with experienced surgeons, high success rates, and affordable treatment options compared to many countries.
Preventing Complications.
Prevention is always better than cure.
- Regular liver check-ups.
- Early treatment of hepatitis.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Vaccinations.
- Managing diabetes and obesity.
- Early detection of cirrhosis can prevent hypotension complications later.
Long-Term Outlook and Recovery.
The prognosis depends on:.
- Stage of cirrhosis.
- Kidney function.
- Response to treatment.
- Overall health.
- With proper management, many patients live stable lives.
- In advanced cases, transplant offers a second chance at life.
Conclusion.
Low blood pressure in cirrhosis is not just a number on a monitor– it’s a warning signal. It tells us that the body is struggling to cope with liver damage.
The good news? Early detection, proper treatment, and lifestyle changes can prevent serious complications. And when cirrhosis reaches an advanced stage, consulting the best liver transplant surgeon in india can open the door to life-saving options.
If you or someone you love has cirrhosis, don’t ignore symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Your body might be asking for help.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).
1. Why does cirrhosis cause low blood pressure?
Cirrhosis widens blood vessels and alters hormone balance, reducing effective blood circulation and lowering BP.
2. Is low blood pressure dangerous in liver patients?
Yes. It can lead to kidney failure, shock, and brain dysfunction if untreated.
3. Can low BP in cirrhosis be reversed?
Mild cases can be managed with medicines and lifestyle changes. Advanced cases may require liver transplant.
4. When should I see a doctor for low BP symptoms?
If you experience frequent dizziness, fainting, confusion, or weakness, seek medical help immediately.
5. Does liver transplant cure low blood pressure permanently?
In many advanced cases, transplant restores normal circulation and significantly improves blood pressure control.