Fatty liver disease is often called a “silent epidemic.” You might not even know you have it until your liver starts waving red flags. So, what’s the big deal about fatty liver disease? Why should you care?
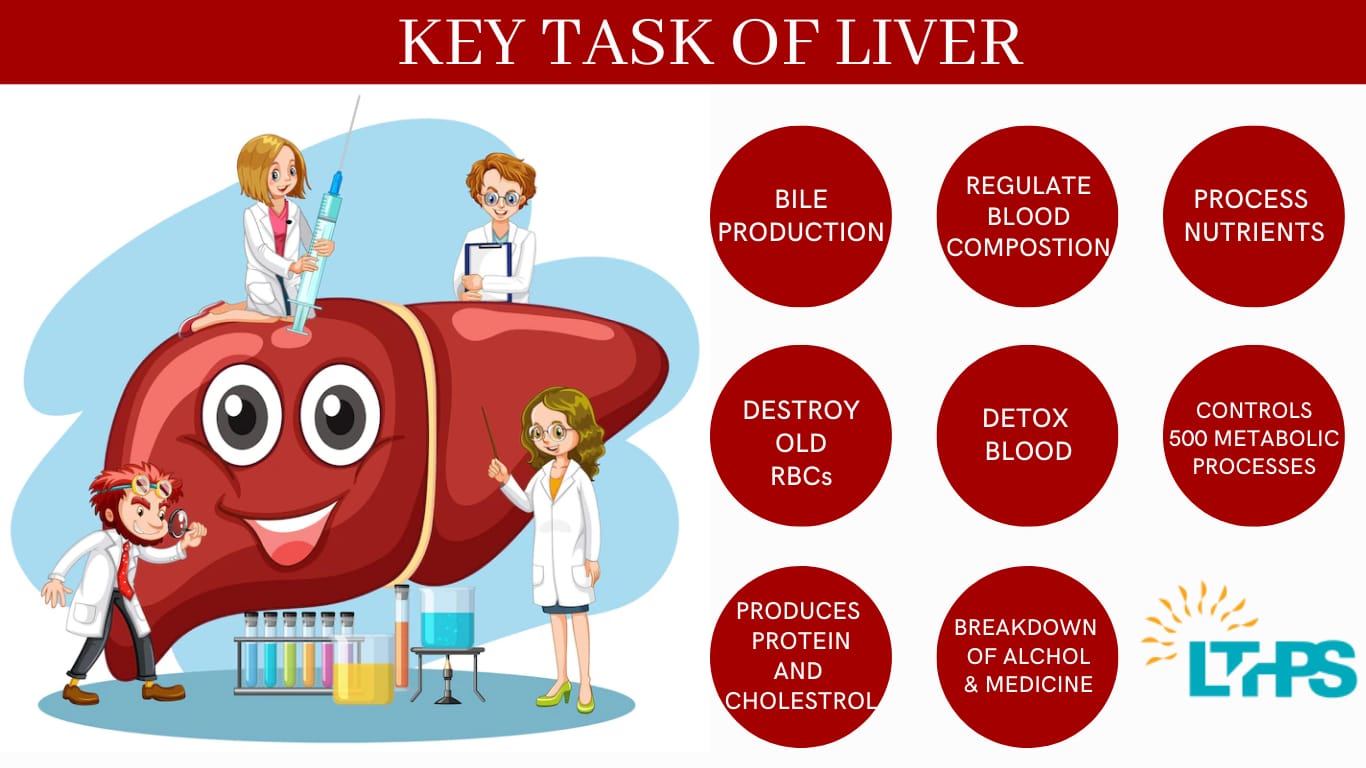
Think of your liver as the body’s waste-processing factory. It handles everything from detoxifying chemicals to producing vital proteins. But when fat builds up in this essential organ, trouble brews.
In this article, we’ll walk you through 8 warning signs of fatty liver disease in simple, easy-to-understand terms. We’ll also explain why early detection is key and when it’s time to consult the best liver transplant surgeon in India
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1 | What Is Fatty Liver Disease? |
| 2 | Why Should You Care About Fatty Liver Disease? |
| 3 | 1. Persistent Fatigue and Weakness |
| 4 | 2. Abdominal Discomfort |
| 5 | 3. Unexplained Weight Loss |
| 6 | 4. Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes (Jaundice) |
| 7 | 5. Swelling in the Abdomen and Legs |
| 8 | 6. Confusion and Trouble Concentrating (Brain Fog) |
| 9 | 7. Elevated Liver Enzymes in Blood Test |
| 10 | 8. Enlarged Liver (Hepatomegaly) |
| 11 | How Is Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosed? |
| 12 | Treatment Options: From Lifestyle to Surgery |
| 13 | When to See the Best Liver Transplant Surgeon in India |
| 14 | Preventing Fatty Liver Disease: Simple Lifestyle Tips |
| 15 | Conclusion |
What Is Fatty Liver Disease?
Imagine your liver is a sponge meant to filter and process nutrients and toxins. Now, picture that sponge soaked not just with water but with excess fat. That’s essentially fatty liver disease– when fat builds up in liver cells.
- There are two main types:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Fat accumulation not caused by alcohol.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Result of heavy alcohol consumption.
- Fatty liver disease is often harmless in early stages but can escalate to serious conditions like cirrhosis or liver failure.
Why Should You Care About Fatty Liver Disease?
Ignoring these warning signs is like ignoring your car’s check engine light. It won’t fix itself. Left unchecked, fatty liver disease can progress silently into irreversible liver damage. Early detection can be your best defence.
- 1. Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
- Do you often feel drained, even after a good night’s sleep? It’s not just stress or ageing. Fat accumulating in your liver hampers its function, leaving you fatigued.
- Why It Happens: Your liver plays a crucial role in energy metabolism. A sluggish liver means your body isn’t converting nutrients into energy efficiently.
- Tip: Notice consistent tiredness and don’t brush it off.
- 2. Abdominal Discomfort
- Ever felt a dull ache in the upper right part of your belly? That’s your liver’s way of speaking up.
- Why It Happens: Swelling of the liver due to fat deposits can cause a feeling of heaviness or discomfort.
- Analogy: It’s like carrying an extra backpack full of bricks that you didn’t ask for.
- 3. Unexplained Weight Loss
- Weight loss is often seen as a good thing, but sudden, unexplained drops can be worrisome.
- Why It Happens: As fatty liver disease progresses, your body struggles to process nutrients, leading to unintended weight loss.
- Tip: Monitor your weight changes closely and consult a doctor if drastic changes occur.
- 4. Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes (Jaundice).
- Noticing a yellow tint in your eyes or skin? Time to pay attention.
- Why It Happens: A dysfunctional liver can’t efficiently process bilirubin, causing it to accumulate in the body.
- Warning: Jaundice is a clear indicator that your liver isn’t doing its job.
- 5. Swelling in the Abdomen and Legs.
- Have you ever seen or felt unexplained puffiness in your legs or belly?
- Why It Happens: Fatty liver disease may lead to fluid buildup due to poor protein production and pressure changes in the liver blood vessels.
- Medical Term: Ascites refers to fluid in the abdomen, while peripheral oedema describes swelling in the legs.
- 6. Confusion and Trouble Concentrating (Brain Fog).
- Do you find yourself forgetting things or struggling to focus?
- Why It Happens: A failing liver can not remove toxins properly, leading to mental confusion, known as hepatic encephalopathy.
- Metaphor: It’s like trying to drive with foggy glasses– you can’t see clearly.
- 7. Elevated Liver Enzymes in Blood Test.
- Have you recently had a routine blood test showing abnormal liver enzyme levels?
- Why It Happens: High levels of ALT (Alanine aminotransferase) and AST (Aspartate aminotransferase) are key indicators of liver inflammation or damage.
Tip: Don’t ignore abnormal lab results. They’re early warnings.
- 8. Enlarged Liver (Hepatomegaly).
- A doctor may detect liver enlargement during a physical exam.
- Why It Happens: As fat accumulates, the liver swells and becomes palpable.
- Important: Early detection can prevent progression to cirrhosis.
- How Is Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosed?
Your doctor will combine your medical history, physical exams, blood tests, and imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI to diagnose fatty liver disease.
Non-invasive Tests: Ultrasound is usually the first step.
- Blood Work: Elevated liver enzymes are often a clue.
- Liver Biopsy: In rare cases, a small sample of liver tissue is taken for detailed analysis.
- Treatment Options: From Lifestyle to Surgery.
- Most cases of fatty liver disease are managed by lifestyle changes, but severe cases may require medical intervention.
- Lifestyle Changes.
- Healthy Diet: Think colourful fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce liver fat.
- Weight Loss: Losing just 5-10% of your body weight can improve liver health.
Medications.
Currently, no FDA-approved drugs specifically target fatty liver disease, but doctors may prescribe medicines to manage underlying conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol.
Surgery.
If the liver damage is severe, a liver transplant becomes necessary. That’s when you must consult the best liver transplant surgeon in India to ensure the best outcomes.
When to See the Best Liver Transplant Surgeon in India.
If your liver disease advances to cirrhosis or liver failure, a liver transplant may be your best option. Signs you should consult a top liver transplant expert include:.
- Persistent jaundice.
- Severe abdominal swelling.
- Confusion or memory issues.
- Rapid deterioration in liver function tests.
- A leading liver transplant surgeon in India can guide you through pre-transplant evaluations, surgery, and post-operative care.
- Preventing Fatty Liver Disease: Simple Lifestyle Tips.
- Prevention is always better than cure. Here’s how you can protect your liver:.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol: Even moderate drinking can contribute.
- Healthy Weight Management: Keep your BMI in check.
- Balanced Diet: Limit sugar and saturated fat intake.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes a day.
- Routine Health Check-ups: Early detection saves lives.
For appointments and consultations:
📞 +91 8527516541
Conclusion.
Fatty liver disease is like a slow-burning fire. It creeps up silently but can cause serious damage if ignored. Recognising the 8 warning signs early can make a world of difference. Simple lifestyle changes, regular check-ups, and seeking medical advice when necessary can keep your liver healthy.
And remember, in advanced cases, the expertise of the best liver transplant surgeon in India could be your lifeline.
FAQs.
1. Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
Yes, in early stages, fatty liver disease is reversible with proper diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
2. Is fatty liver disease dangerous?
It can be. If untreated, it may progress to cirrhosis or liver failure, requiring a transplant.
3. How is fatty liver disease detected?
Doctors typically use blood tests, ultrasounds, and sometimes liver biopsies to diagnose it.
4. What foods should I avoid to prevent fatty liver disease?
Avoid sugary drinks, processed foods, and excessive alcohol. Focus on fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
5. When should I consult a liver transplant surgeon?
Consult a specialist when you experience persistent jaundice, abdominal swelling, or when liver function tests show rapid decline.